tibial torsion measurement special test|tibial torsion in adults : mail order to test the calcaneofibular ligament the examiner will adduct and invert the . Resultado da Girar a roda é um jogo comum ou mecanismo de tomada de decisão em que uma roda é girada e um ponteiro, marcador ou outro indicador é usado para selecionar aleatoriamente um valor ou resultado de um conjunto de opções possíveis. . Sim! Quando você clica na roda, ela acelera por exatamente .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Aprenda a calcular o retorno de suas apostas com Dutching, um método que consiste em fazer apostas simultâneas em vários resultados para garantir igual lucro em todas as .
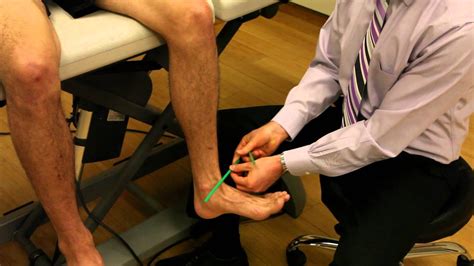
tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knees flexed to 90° over the edge of the examining table. the examiner places the thumb of one hand over the apex of one malleolus and the index finger of the same hand over the apex of the other malleolus.Special Test: Mortons Neuroma aka Metatarsal Squeeze Test: Video .to test the calcaneofibular ligament the examiner will adduct and invert the .
Orthopedic Exam/ Special Test: Ramirez’s Test PROCEDURE: patient is supine, .
tibial torsion special test
Heel Thump Test: PROCEDURE: the patient is in seated or supine; the .Tibial Torsion Test; Tinel’s Sign (Ankle) Deltoid Ligament Test. Orthopedic Exam .Special Test:Posterior Drawer Test (Ankle) PROCEDURE: •Patient is supine with .Ankle Special Test for Orthopedic Examination: Special Test: Anterior .
Tibial Torsion Test; Tinel’s Sign (Ankle) Thompson’s Test / Simmond’s Test. . Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .
Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90° and foot resting in its natural position. The TFA is measured . Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibri.
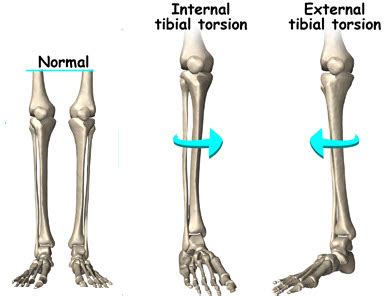
Our results showed that clinical measurements of tibial torsion differences are highly accurate and have a great inter- and intra-observer reliability. Intraoperative tools for . External Tibial Torsion. External tibial torsion usually presents between four and seven years of age when the tibia externally rotates during normal growth and worsens into a deformity.
The proposed radiographic measurement is a practical method for evaluation of tibial torsion in outpatient clinics without the need for specialized equipment. Level of . A transmalleolar axis that is externally rotated more than 20° signifies external tibial torsion, and a transmalleolar axis externally rotated less than 10° signifies internal tibial .To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90°. Typically the foot axis is 10° .
Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibri.
Drexler et al conducted a study to evaluate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of 12 patients (15 knees) undergoing tibial derotation osteotomy and tibial tuberosity transfer for recurrent patella subluxation associated with excessive external tibial torsion. [] Clinical evaluation was carried out using preoperative and postoperative Knee Society Score, Kujala .To Measure Q Angle: • Patient is standing or supine, with the knee in extension (femur neutral: no internal or external rotation) and patient’s feet in a neutral position (no pronation or supination). Normal Test Result: A normal Q angle . Femoral and tibial torsion is generally measured on axial CT images. Several measurement techniques have been proposed [15-28].For femoral torsion the measurement technique described by Hernandez et al. [] and for tibial torsion the intermalleolar measurement technique described by Goutallier et al. [] have been reported to be particularly reliable [].
2.1 Femoral Torsion. 2.1.1 Special topic: . Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. . Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90 . Tibial torsion test in sitting position. Tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knee flexed to 90’over the edge of the examining table. The examiner has put the thumb of one hand over the apex of the one malleolus. Next, the examiner visualizes the axes of the knee & of the ankle. trochanteric prominence angle test . . tibial torsion. look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- mean 5° internal (range, −30° to +20°) normal value at age 8 years- mean 10° external (range, −5° to +30°) metatarsus adductus. Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures.
Measurements more than 2 standard deviations outside the mean may suggest femoral anteversion or retroversion, or internal or external tibial torsion Thigh-foot angle ( Figure 4 ) Angular measurements
Internal tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the tibia, which leads to in-toeing of the foot. . To protect your loved one, please do not visit if you are sick or have a COVID-19 positive test result. Get more resources on masking and COVID-19 precautions . Internal tibial torsion can be diagnosed through a physical exam and measurements .
Special Tests | Orthopedic Examination for Physical Therapy: Video Demos, Purpose, Procedure & Techniques for Assessment. . Tibial Torsion Test; Tinel’s Sign (Ankle) Health History – Review of Systems. . Range of motion tests are used to measure how well a patient can move a joint. Some joints like the thumb hips, and shoulder have a .torsion and 3.9° (0.0°–15.0°) for tibial torsion. Mean interreader differences at CT were 3.3° (0.0°–9.0°) for femoral and 3.0° (0.0°–10.0°) for tibial torsion. There was no trend for larger intermethod differences with decreasing age of the children. CONCLUSION. Femoral and tibial torsion measurements in children using 3D models At present, owing to the lack of a universally and consistently applied, accurate method of measurement, normal values of tibial torsion amongst the normal population are unknown and there is unsurprisingly high variability in the values reported. Jakob et al 16 reported mean tibial torsion to be 30° external, which is similar to the present .
compression deflection test
compression force deflection test
Create Personal Test Create Group Test . external tibial torsion / pronated feet. anatomical factors. osseous. patella alta. . measures the distance between 2 perpendicular lines from the posterior cortex to the tibial tubercle and the trochlear groove These special tests are used in creating a proper treatment plan or therapy for a patient's injury or condition. . Tibial Torsion Test; Tinel’s Sign (Ankle) What are Special Tests? . Range of motion tests are used to .
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. . Braces or special shoes. Surgery. Key points about tibial torsion in children. Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the .
Tibial torsion measurements were obtained using goniometry and three-dimensional kinematics based on the Plug-in Gait model. . the professional experience of the person who performed the test may lead to measurement differences.19. . An excessive external or internal tibial torsion when presented requires special attention to determine its .Rotatory malalignment of the lower extremity in childhood is a very common clinical problem. This malalignment is most frequently due to tibial torsion. Despite the frequency of tibial torsional malalignment, proposed methods of assessment have not found clinical application and the natural history of the deformity is incompletely understood.
measurement modalities. Except for one measurement of femoral torsion and one measure-ment of tibial torsion, all results based on the 3D models were within the 95% limit of agree - ment (mean ± 1.96 SD). Interreader agreement was statistically significant (p < 0.001) for all measurements with high intraclass correlation coefficients (> 0.9). Pathological tibial torsion is known to negatively influence the functionality of the lower extremity, and therefore, its assessment might play an important role. While 3D imaging is used for many examinations of the musculoskeletal system, for the determination of tibial torsion no 3D measurement technique has been available so far. We developed a 3D measurement . Measurement of tibial torsion is done along the longitudinal axis of the tibia and is measured in comparison to the uninjured side. A discrepancy of more than 10° is defined according to most authors as malrotation [2–5, 9–11]. Currently, computed tomography is accepted as gold standard procedure for determining tibial torsion [2, 9, 12–16].
OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the interchangeability and reliability of femoral and tibial torsion measurements in children using 3D models based on biplanar radiography compared with CT measurements. MATERIALS AND METHODS. Femoral and tibial torsion were measured in 50 patients (mean age, 10.9 years; range, 4.7–14.8 .
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shin bones (the bones that are located between the knee and the ankle). Tibial torsion causes the child's feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a "pigeon-toed" appearance. . Occasionally, braces or special shoes are prescribed by the doctor. Long-term outlook for tibial torsion. Tibial . Special Test for Tibial Torsion. Tibial Torsion Test. Special Tests for Ligamentous Instability. Anterior Drawer Test. Prone Anterior Drawer Test. Talar Tilt Test. External Rotation Stress Test (Kleiger Test) Other Special Tests. . Any measurement greater than 10 mm is considered abnormal. No statistically significant difference between the measurements of the two methods was detected by Bland-Altman plots. With the exception of one measurement of femoral torsion, one measurement of tibial torsion and one measurement of femorotibial torsion, all EOS imaging measurements were within the 95% limits of agreement (the mean ± 1.96 SD).Doctors can detect this birth defect by doing a physical examination and taking various measurements of the legs. In most children, the shinbone returns to a normal position without treatment around 5 to 6 years of age. Children who have a severe case of tibial torsion may need to wear special shoes, a cast, or leg braces.
Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .
tibial torsion in adults
physical therapy for tibial torsion
Ontario's Best Store for Geeks, Collectors, and Pop-Culture Enthusiasts In our stores you'll find a massive selection of Funko, Manga, Comics, Board Games, Plush, DD, Anime .
tibial torsion measurement special test|tibial torsion in adults